JAKARTA, opinca.sch.id – Carbon Credits: Financial Instruments for Environmental Impact—sounds like textbook stuff, right? Stick with me, I promise it’s more exciting (and more real) than you’d think. I’ve been semi-obsessed with these ever since my old office tried to ‘go green’ and ended up buying credits that, well, had zero legit impact. Let’s talk about why that happened—and how you can avoid those mistakes.
Carbon credits have emerged as vital financial instruments in the global effort to combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By allowing companies and countries to buy and sell credits that represent a reduction in carbon dioxide emissions, these credits create a market-driven approach to environmental sustainability. This article explores the significance of carbon credits, their mechanisms, and why they matter in the fight against climate change.
1. Understanding Carbon Credits
Carbon credits are licenses that enable the holder to release a specified quantity of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. One carbon credit typically represents the right to emit one metric ton of carbon dioxide. The concept is rooted in cap-and-trade systems, where a limit (cap) is set on total emissions, and companies can trade credits to meet their obligations. Key components include:
- Cap-and-Trade Systems: Governments or regulatory bodies set a cap on emissions for specific sectors, distributing or auctioning off credits to companies. Those that reduce emissions below their cap can sell excess credits to others that exceed their limits.
- Voluntary Markets: In addition to regulatory frameworks, voluntary markets exist where companies and individuals can purchase carbon credits to offset their emissions, even if not legally required to do so.
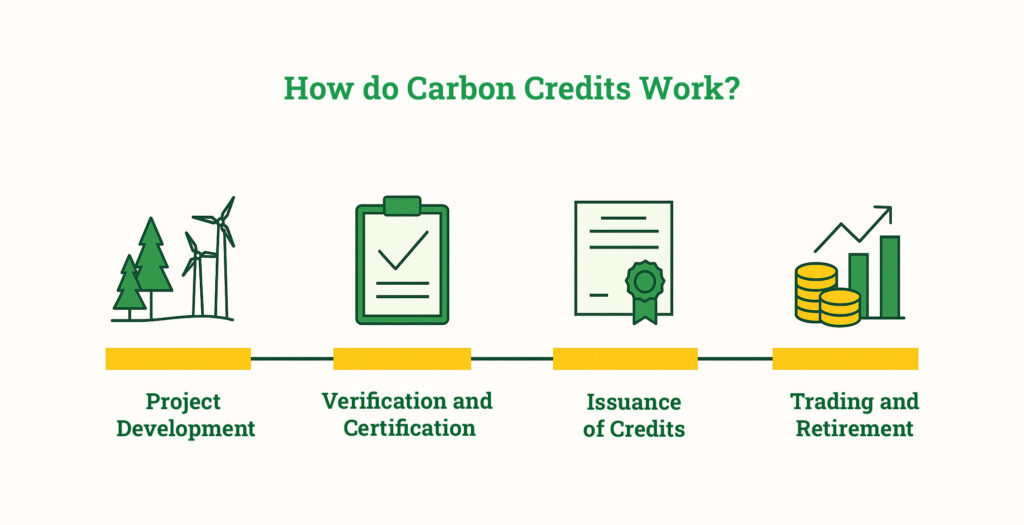
2. The Mechanism of Carbon Credits
The carbon credit system operates through several steps:
- Emission Reduction Projects: Organizations undertake projects that reduce emissions, such as reforestation, renewable energy installations, or energy efficiency improvements. These projects must meet specific criteria and undergo verification.
- Certification: Once a project demonstrates a quantifiable reduction in emissions, it is certified by a recognized authority, generating carbon credits based on the amount of CO2 reduced.
- Trading: Companies can buy and sell these credits on various exchanges or through direct agreements, allowing for flexibility in how they meet their emissions targets.
3. The Importance of Carbon Credits
Carbon credits play a crucial role in addressing climate change for several reasons:
– Encouraging Investment in Green Technologies
By monetizing carbon reductions, carbon credits incentivize businesses to invest in cleaner technologies and practices. This investment leads to innovation and the development of sustainable solutions that can further reduce emissions.
– Fostering Accountability
Carbon credits create a financial incentive for companies to monitor and report their emissions. This accountability encourages organizations to adopt more sustainable practices and strive for continuous improvement.
– Supporting Global Emission Reduction Goals
Carbon credit systems contribute to international climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, by allowing countries to meet their emission reduction targets collaboratively. This flexibility enables nations to pursue cost-effective strategies for reducing global emissions.
4. Addressing Criticisms of Carbon Credits
While carbon credits offer significant benefits, they are not without criticism. Some common concerns include:
– Potential for Greenwashing
Companies may purchase carbon credits as a way to offset their emissions without making meaningful changes to their operations. This practice, known as greenwashing, can undermine the effectiveness of carbon markets. To address this, it is essential to ensure rigorous verification and transparency in the certification process.
– Market Volatility
The carbon credit market can be subject to fluctuations in price and demand, which may affect the stability and predictability of investments in emission reduction projects. Establishing robust regulatory frameworks can help mitigate these risks.
– Limited Scope
Carbon credits primarily focus on carbon dioxide emissions, potentially neglecting other greenhouse gases and environmental issues. A comprehensive approach to sustainability should consider a broader range of environmental impacts.
5. Why Carbon Credits Matter
Despite the criticisms, carbon credits matter for several compelling reasons:
– Driving Systemic Change
Carbon credits create a market mechanism that aligns economic incentives with environmental goals. By integrating environmental costs into business decisions, carbon credits promote a shift toward sustainable practices across industries.
– Mobilizing Resources for Climate Action
The financial flows generated through carbon credit trading can fund vital projects that address climate change, such as renewable energy initiatives, reforestation efforts, and community-based sustainability programs.
– Empowering Individuals and Organizations
Carbon credits provide a tangible way for individuals and businesses to take responsibility for their carbon footprint. By purchasing credits, they can contribute to global efforts to mitigate climate change, fostering a sense of agency and involvement in environmental stewardship.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, carbon credits are more than just financial instruments; they represent a crucial mechanism for driving environmental impact and fostering sustainable practices. By encouraging investment in green technologies, promoting accountability, and supporting global emission reduction goals, carbon credits play a significant role in the fight against climate change. While challenges and criticisms exist, the potential of carbon credits to mobilize resources for climate action and empower individuals and organizations makes them a vital component of our collective efforts to create a more sustainable future. As we navigate the complexities of addressing climate change, recognizing the importance of carbon credits will be essential in building a resilient and environmentally responsible economy.
Explore our “Financial” category for more insightful content!
Don't forget to check out our previous article: Insurance Reimbursement Processes: A Guide for Hospitals
