JAKARTA, opinca.sch.id – Currency Swaps: Exchanging Financial Obligations Across Currencies sounds intimidating, right? Honestly, the first time I heard the term “currency swaps,” I had to triple-check if I understood it. Turns out, once you get past the jargon, it’s super interesting—especially when you see how global companies and even my old work team use it to keep business running smooth.
Currency swaps are financial instruments that allow parties to exchange cash flows in different currencies, typically involving the exchange of principal and interest payments. These swaps can be valuable tools for managing currency risk, optimizing financing costs, and enhancing liquidity. In this guide, we will explore the mechanics of currency swaps, their benefits, and how you can effectively utilize them to meet your financial objectives.
1. Understanding Currency Swaps
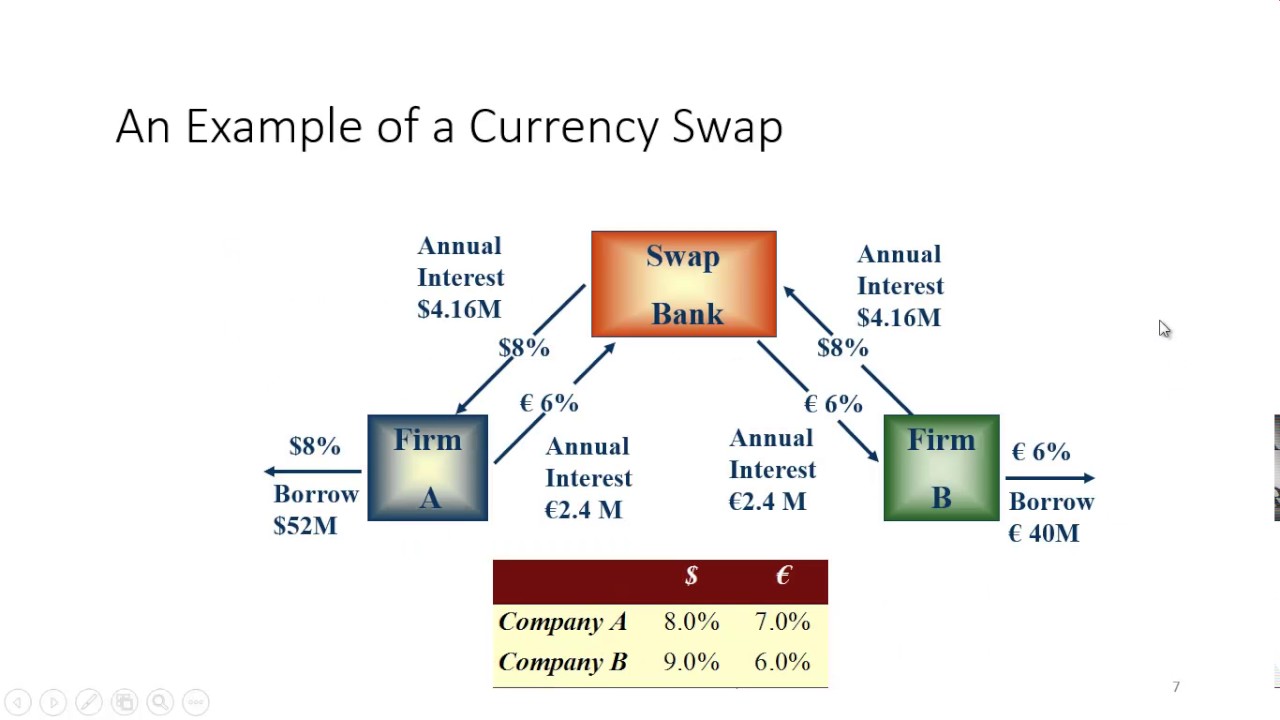
A currency swap is a financial agreement between two parties to exchange principal and interest payments in different currencies. Typically, one party pays interest in one currency, while the other party pays interest in another currency. At the end of the swap agreement, the principal amounts are exchanged back at the original exchange rate.
Key Components of Currency Swaps:
- Principal Amounts: The initial amounts exchanged between the parties, often based on the notional value of the currencies involved.
- Interest Payments: The periodic interest payments made by each party, calculated based on the principal amounts and the respective interest rates.
- Maturity Date: The date on which the currency swap agreement ends, and the principal amounts are exchanged back.
2. How Currency Swaps Work
The mechanics of a currency swap can be illustrated through a simple example:
- Initial Exchange: Two companies, Company A (based in the U.S.) and Company B (based in Europe), agree to a currency swap. Company A wants to borrow euros, while Company B wants to borrow U.S. dollars.
- Principal Exchange: At the start of the agreement, Company A exchanges a specified amount of U.S. dollars for euros with Company B.
- Interest Payments: Throughout the life of the swap, each company pays interest on the principal amount in the currency they received. For example, Company A pays interest in euros, while Company B pays interest in U.S. dollars.
- Final Exchange: At the maturity date, the companies exchange the principal amounts back to their original currencies.
Example: If Company A swaps $10 million for €9 million, it will pay interest on €9 million, while Company B pays interest on $10 million. At the end of the swap, they will exchange the principal amounts back.
3. Benefits of Currency Swaps
Currency swaps offer several advantages for businesses and financial institutions:
– Hedging Against Currency Risk
Currency swaps can help mitigate exposure to fluctuations in exchange rates. By locking in exchange rates for future cash flows, companies can protect themselves from adverse currency movements.
Insight: For instance, a U.S. company with euro-denominated revenue can use a currency swap to convert its euro cash flows into dollars, reducing the risk of currency depreciation.
– Cost Optimization
Currency swaps can enable companies to access cheaper financing options in different currencies. By swapping currencies, businesses can take advantage of favorable interest rates in foreign markets.
Example: If a company can borrow at a lower interest rate in euros than in dollars, it can enter into a currency swap to benefit from the lower rate while still meeting its dollar obligations.
4. Risks Associated with Currency Swaps
While currency swaps have many benefits, they also come with certain risks that participants should be aware of:
– Counterparty Risk
There is a risk that one party may default on its obligations, leading to potential losses for the other party. It is essential to conduct thorough due diligence on the counterparty’s creditworthiness before entering into a swap agreement.
– Market Risk
Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the value of the swap. If the market moves unfavorably, one party may end up paying more than anticipated.
Tip: Regularly monitor market conditions and be prepared to adjust your strategy if necessary.
5. Practical Applications of Currency Swaps
Currency swaps can be utilized in various scenarios to achieve specific financial goals:
– International Expansion
Companies looking to expand into foreign markets can use currency swaps to manage the financial implications of operating in different currencies. This can include financing investments or hedging revenue streams.
Example: A U.S. company expanding into Europe may enter a currency swap to secure euros for its operations while minimizing currency risk.
– Debt Management
Organizations can use currency swaps to refinance existing debt or optimize their capital structure. By exchanging currencies, they can take advantage of lower interest rates or improve their debt profile.
Real Story: A multinational corporation facing high-interest payments on foreign debt used a currency swap to convert its obligations into a more favorable currency, reducing overall financing costs.
6. Conclusion
Currency swaps are powerful financial instruments that can help businesses manage currency risk, optimize financing costs, and enhance liquidity. By understanding the mechanics, benefits, and risks associated with currency swaps, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial objectives.
As you consider utilizing currency swaps, remember to conduct thorough research and seek expert advice to ensure that you are making the best choices for your financial strategy. With careful planning and execution, currency swaps can be an effective tool for achieving your financial goals across different currencies.
Boost Your Competence: Uncover Our Insights on Financial
Spotlight Article: “Repurchase Agreements: Short-Term Financial Borrowing!”
