Asset allocation is a crucial investment strategy that involves distributing investments across various asset classes to manage risk and optimize returns. By diversifying a portfolio, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility on their overall wealth. This article delves into the importance of asset allocation, the different asset classes, and strategies for effective diversification.
Importance of Asset Allocation
1. Risk Management
Proper asset allocation helps mitigate risks associated with market fluctuations.
- Volatility Reduction: By spreading investments across various asset classes, investors can cushion their portfolios against significant losses during market downturns.
- Stability: A well-diversified portfolio tends to provide more stable returns over time, reducing the likelihood of drastic swings in value.
2. Enhanced Returns
Strategic asset allocation can lead to improved long-term returns.
- Optimizing Growth: Allocating funds to higher-risk assets like stocks can enhance growth potential, while including safer assets like bonds can provide stability.
- Adjusting for Goals: Different asset allocations can align with individual investment goals, whether they focus on growth, income, or capital preservation.
3. Adaptability
Asset allocation allows investors to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Rebalancing: Regularly reviewing and rebalancing a portfolio ensures that it remains aligned with an investor’s risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Responding to Economic Changes: Investors can adjust their allocations in response to economic indicators, interest rates, and market trends.
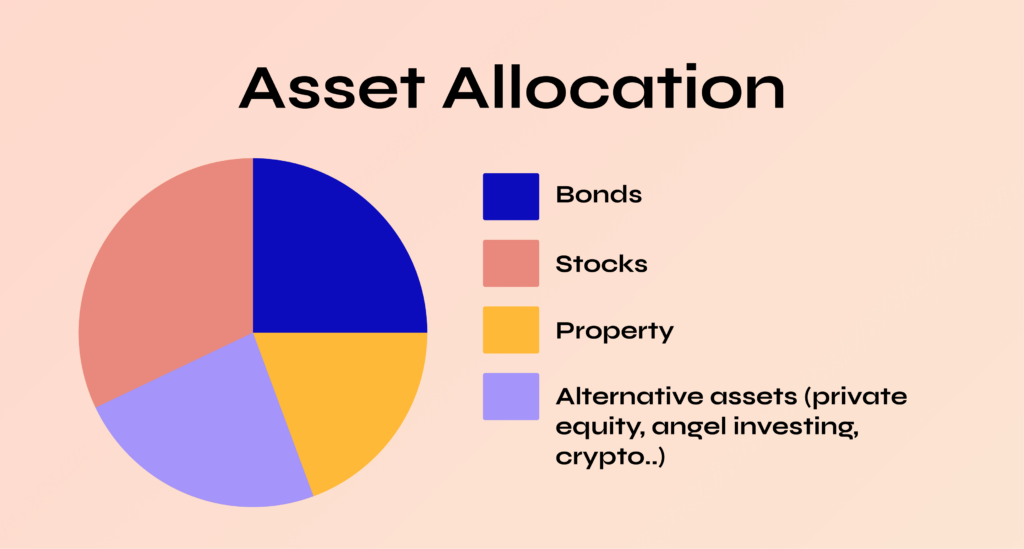
Different Asset Classes
1. Equities (Stocks)
- Growth Potential: Stocks offer high potential returns but come with higher volatility.
- Types: Common stocks, preferred stocks, and international equities.
2. Fixed Income (Bonds)
- Stability and Income: Bonds provide regular interest payments and are generally less volatile than stocks.
- Types: Government bonds, corporate bonds, municipal bonds, and high-yield bonds.
3. Cash and Cash Equivalents
- Liquidity: Investments in cash or cash equivalents (like money market funds) provide liquidity and safety.
- Low Returns: While safer, these typically offer lower returns compared to other asset classes.
4. Real Estate
- Tangible Asset: Real estate can provide rental income and potential appreciation.
- Diversification: Investing in real estate can diversify a portfolio beyond traditional financial assets.
5. Alternative Investments
- Diversification Beyond Traditional Assets: Includes commodities, hedge funds, private equity, and collectibles.
- Risk and Return Profiles: These can have different risk-return characteristics, adding further diversification.
Strategies for Effective Diversification
1. Determine Risk Tolerance
- Assess Personal Risk: Understand how much risk you are willing to take based on your investment goals, time horizon, and financial situation.
- Use Risk Assessment Tools: Many financial institutions offer questionnaires to help determine risk tolerance.
2. Set Investment Goals
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline your financial goals, whether they are short-term (buying a home) or long-term (retirement savings).
- Align Allocation: Tailor your asset allocation strategy to meet these specific goals.
3. Diversify Within Asset Classes
- Variety of Investments: Within each asset class, diversify further. For example, in equities, consider large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks across different sectors.
- Geographic Diversification: Include international investments to mitigate country-specific risks.
4. Regularly Review and Rebalance
- Monitor Performance: Regularly assess the performance of your investments to ensure they align with your goals.
- Rebalance as Needed: Adjust your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation, especially after significant market movements.
5. Stay Informed
- Keep Up with Market Trends: Stay informed about economic conditions, market trends, and financial news that may impact your investments.
- Educate Yourself: Continuously seek knowledge about investment strategies and asset classes.
Conclusion
Asset allocation is a vital strategy for reducing risk and enhancing returns in investment portfolios. By diversifying across various asset classes—such as equities, fixed income, cash, real estate, and alternatives—investors can better manage market volatility and align their investments with their financial goals. Regular monitoring and rebalancing, combined with a clear understanding of risk tolerance and investment objectives, are key to successful asset allocation. Ultimately, a well-structured asset allocation strategy can pave the way for long-term financial success and stability.
Read Also About Financial forecasting is a critical tool used by businesses and organizations to predict their future financial performance based on historical data, market trends, and economic conditions.
